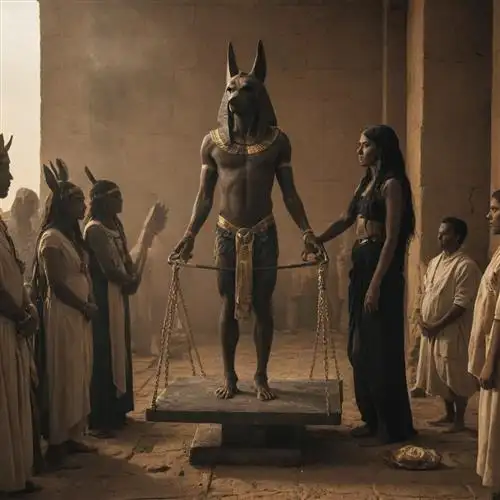The Jackal Deity Anubis
Anubis, the enigmatic jackal-headed deity, holds a revered place in the pantheon of Ancient Egyptian mythology. As the god associated with mummification and the protection of the dead, Anubis played a crucial role in the intricate rituals and beliefs that guided the Egyptians' journey into the afterlife.
At the core of Anubis' significance lies his connection to the process of embalming and the transition from life to death. As the patron of embalmers, Anubis oversaw the meticulous mummification procedures, ensuring the preservation of the deceased's physical form. This intimate involvement with the dead cemented Anubis' status as a gatekeeper, guiding the souls of the departed into the next realm.
Beyond his role in the afterlife, Anubis was also revered as a protector and judge of the dead. In the pivotal "Weighing of the Heart" ceremony, Anubis would oversee the judgment of the deceased, weighing their heart against the feather of Ma'at, the goddess of truth and justice. This sacred ritual determined the worthiness of the individual, granting them passage into the eternal realm or condemning them to a fate of eternal damnation.
The iconography associated with Anubis is equally intriguing, with the jackal-headed deity often depicted wearing a distinctive crown and holding various symbolic objects. The jackal, a scavenger known to frequent cemeteries, was believed to have a heightened connection to the realm of the dead, making it an apt representation of Anubis' domain.
Anubis' influence extended beyond the borders of Ancient Egypt, with the deity's reverence and symbolism reaching as far as the Greco-Roman world. The Greeks, in particular, associated Anubis with the underworld god Hades, further solidifying the jackal deity's status as a powerful and enduring figure in the ancient world.
The Role of Anubis in Funerary Rites
Anubis, the jackal-headed Egyptian deity, held a pivotal role in the funerary rites and rituals of ancient Egypt. As the god associated with the process of mummification and the protection of the dead, Anubis was a central figure in the journey of the deceased into the afterlife.
One of Anubis' primary responsibilities was the mummification of the deceased. He was believed to have taught the techniques of embalming and preservation, ensuring the physical body was prepared for the transition to the afterlife. Anubis would oversee the complex process, which involved removing the internal organs, drying the body, and wrapping it in linen bandages. This meticulous preparation was crucial, as the Egyptians believed the preservation of the physical form was essential for the soul's continued existence.
In addition to his role in mummification, Anubis was also responsible for guiding the deceased through the dangerous and uncertain realm of the afterlife. During the funerary rites, Anubis would accompany the deceased to the Hall of Judgement, where the soul's worthiness would be assessed by the gods. Anubis would weigh the heart of the deceased against the feather of truth, symbolizing the balance between the individual's actions and the principles of Ma'at (cosmic order and justice).
If the deceased's heart was deemed pure and virtuous, Anubis would then lead the soul to the realm of the afterlife, known as the Field of Reeds. Here, the deceased would be reunited with their loved ones and live in a peaceful, idyllic existence. Anubis' presence during this critical transition was believed to provide protection and guidance, ensuring the deceased's safe passage to the afterlife.
Anubis' significance in funerary rites was further reinforced by his widespread representation in ancient Egyptian art and architecture. Statues, reliefs, and wall paintings depicting Anubis were commonly found in tombs, temples, and funerary complexes, highlighting his central role in the rituals and beliefs surrounding death and the afterlife.
Anubis and the Weighing of the Heart
The role of Anubis in the Egyptian funerary rite known as the "Weighing of the Heart" is a profound and integral aspect of the deity's significance in ancient Egyptian mythology. As the jackal-headed god associated with embalming and the afterlife, Anubis was responsible for guiding the deceased through the intricate process of mummification and ensuring the safe passage of the soul into the next world.
At the heart of this ritual was the belief that the deceased's heart would be weighed against the feather of Ma'at, the goddess of truth, justice, and cosmic order. This symbolic act was crucial in determining the fate of the soul. If the heart was found to be pure and balanced, the individual was deemed worthy of eternal life in the realm of the afterlife. However, if the heart was deemed too heavy with sins or misdeeds, it would be devoured by the fearsome demon Ammit, condemning the soul to oblivion.
Anubis played a central role in this pivotal moment, acting as the mediator between the mortal and divine realms. As the one who presided over the weighing of the heart, Anubis was responsible for carefully monitoring the delicate balance of the scale, ensuring that justice was served. His keen eyesight and unwavering attention to detail were essential in this solemn ritual, as the slightest imbalance could determine the fate of the soul.
Moreover, Anubis was also believed to possess the ability to intercede on behalf of the deceased, pleading their case before the Ennead, the council of nine major deities in the Egyptian pantheon. This intercessory role was crucial, as it provided the deceased with the opportunity to argue their case and potentially sway the outcome of the weighing process.
Anubis in Modern Popular Culture
Anubis, the jackal-headed deity, has remained a powerful and enduring icon in ancient Egyptian culture, and his influence has continued to captivate the modern world. While his importance in ancient Egyptian mythology is well-documented, his presence in modern popular culture is equally fascinating. From films and television shows to video games and fashion, Anubis has seamlessly transitioned into the contemporary zeitgeist, solidifying his status as a timeless and versatile symbol.
One of the most notable ways Anubis has permeated modern popular culture is through his representation in various forms of media. In the realm of cinema, the jackal-headed deity has been featured prominently in numerous films, often serving as a mystical and enigmatic figure that adds an air of ancient mysticism to the narrative. For instance, the character of Imhotep in the "The Mummy" franchise, with his strong ties to Anubis, has become a beloved and iconic figure among fans of the genre. Similarly, the character of Anck-Su-Namun, the lover of Imhotep, has captivated audiences with her tragic story and her association with the Anubis deity.
Beyond the silver screen, Anubis has also found a home in the world of video games, where his likeness and mythology have been expertly woven into the gameplay and storytelling. Titles such as the "Assassin's Creed" series and "Lara Croft: Tomb Raider" have incorporated Anubis as a central figure, allowing players to delve deeper into the rich and complex mythology of ancient Egypt. These virtual representations not only entertain but also educate, sparking a renewed interest in the ancient Egyptian culture and the significance of Anubis within it.
In the realm of fashion and design, Anubis has also left an indelible mark. The jackal-headed deity has been a source of inspiration for numerous designers, who have incorporated his iconic image into their collections. From high-end couture to streetwear, Anubis-inspired motifs and patterns have become a staple, reflecting the enduring fascination with this ancient Egyptian icon. Fashion brands and luxury labels have tapped into the allure of Anubis, creating a sense of mysticism and cultural relevance that resonates with modern audiences.
Moreover, Anubis has found a home in the realm of the occult and esoteric practices. In certain New Age and neopagan movements, the jackal-headed deity has been embraced as a symbol of transformation, death, and the afterlife. This association has led to the incorporation of Anubis imagery and rituals into various spiritual practices, further cementing his status as a powerful and multifaceted icon in the modern cultural landscape.